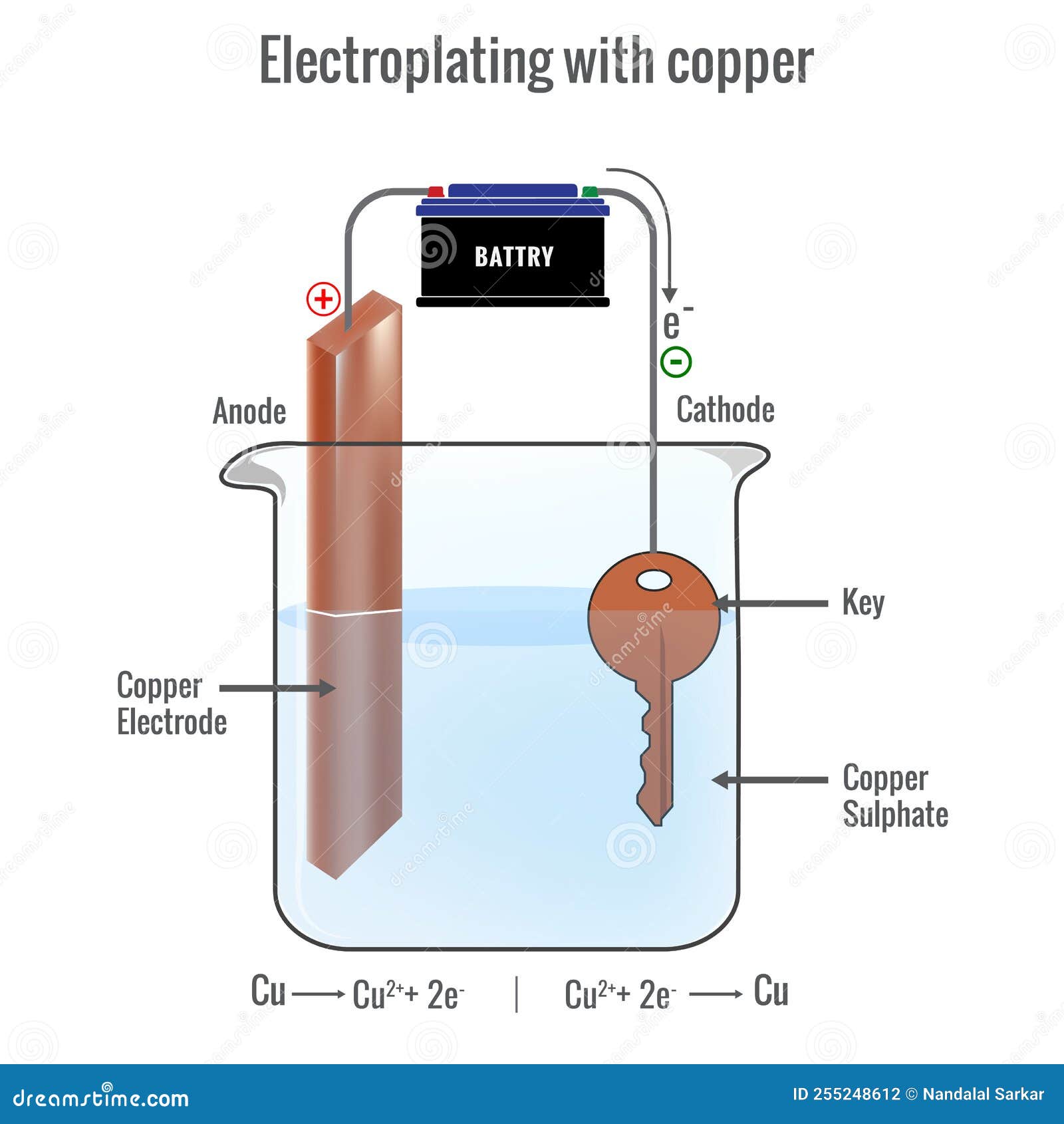
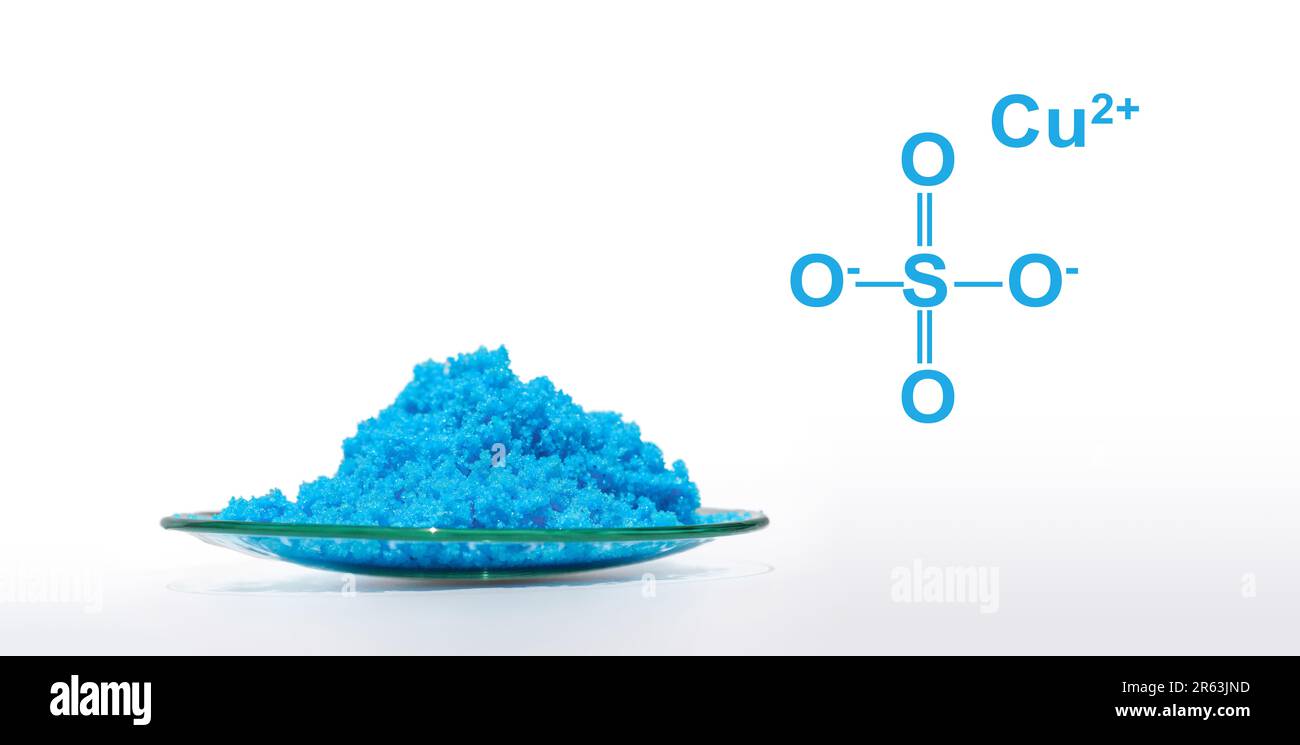
Copper(I) sulfate, also known as cuprous sulfate, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Cu2SO4. It is a white solid, in contrast to copper(II) sulfate, which is blue in hydrous form. Compared to the commonly available reagent, copper(II) sulfate, copper(I) sulfate is unstable and not readily available.
Structure
Cu2SO4 crystallizes in the orthorhombic space group Fddd. Each oxygen in a sulfate anion is bridged to another sulfate by a copper atom, and the Cu−O distances are 196 pm.
Synthesis
Cuprous sulfate is produced by the reaction of copper metal with sulfuric acid at 200 °C:
- 2 Cu 2 H2SO4 → Cu2SO4 SO2 2 H2O
Cu2SO4 can also be synthesized by the action of dimethyl sulfate on cuprous oxide:
- Cu2O (CH3O)2SO2 → Cu2SO4 (CH3)2O
The material is stable in dry air at room temperature but decomposes rapidly in presence of moisture or upon heating. It decomposes into copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate upon contact with water.
- Cu2SO4 5 H2O → Cu CuSO4 · 5 H2O
References


-sulfate-3D-vdW.png)